We use dataframes to handle tabular data in python. Sometimes, we might need to compare different dataframes according to values in their columns for each record. In this article, we will discuss how we can compare two dataframes in python.
How to Compare Two DataFrames in Python?
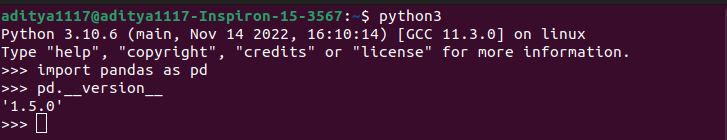
To compare two pandas dataframe in python, you can use the compare() method. However, the compare() method is only available in pandas version 1.1.0 or later. Therefore, if the codes in this tutorial don’t work for you, you should consider checking the version of the pandas module on your machine. For this, you can execute the following code.
import pandas as pd
pd.__version__Output:
If the pandas’ version in your machine is older than 1.1.0, you can upgrade it using PIP as shown below.
pip3 install pandas --upgradeFor python2, you can use pip instead of pip3 in the above command.
The compare() Method
The compare() method, when invoked on a dataframe object, takes the second dataframe as its first input argument and three optional input arguments. The syntax for the compare() method is as follows.
df1.compare(df2, align_axis=1, keep_shape=False, keep_equal=False)Here,
df1is the first dataframe.- The parameter
df2denotes the second dataframe to whichdf1is to be compared. - The parameter
align_axisis used to decide whether we need to compare rows or columns. By default, it has the value 1, which means that the output is shown by comparing the columns. If the value 0 is assigned to thealign_axisparameter, the comparison results are shown by comparing rows. - The parameter
keep_shapeis used to decide if we want to display all the columns of the data frames or only the columns with different values for each row in the input dataframes. It has the default value of False, which means that only the columns with different values for each row will be shown in the resultant dataframe. If you want to display all the columns of the dataframe, you can pass the value True as an input argument to thekeep_shapeparameter. - If the values in a column of the rows that are being compared are equal, NaN is assigned as the resultant value of the column in the comparison data frame. To keep the original values instead of the NaN values, we use the
keep_equalparameter. Thekeep_equalparameter has the default value False, which means that the columns that have equal values will be assigned the value NaN in the resultant dataframe. To keep the original values for the columns that have equal values, you can assign the value True to thekeep_equalparameter.
Compare Pandas DataFrames Column-wise
To compare the dataframes so that the output values are organized horizontally, you can simply invoke the compare() method on the first dataframe and pass the second dataframe as the input argument as shown in the following example.
import pandas as pd
myDicts1=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 82},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":75, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":87, "Physics":84, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 84},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":79, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df1=pd.DataFrame(myDicts1)
print("The first dataframe is:")
print(df1)
myDicts2=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":95, "Physics":92, "Chemistry": 75},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":73, "Physics":98, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":88, "Physics":85, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":99, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":70, "Chemistry": 96},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":89, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df2=pd.DataFrame(myDicts2)
print("The second dataframe is:")
print(df2)
output_df=df1.compare(df2)
print("The output dataframe is:")
print(output_df)Output:
The first dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 87 82
1 2 75 100 90
2 3 87 84 76
3 4 100 100 90
4 5 90 87 84
5 6 79 75 72
The second dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 95 92 75
1 2 73 98 90
2 3 88 85 76
3 4 100 99 90
4 5 90 70 96
5 6 89 75 72
The output dataframe is:
Maths Physics Chemistry
self other self other self other
0 100.0 95.0 87.0 92.0 82.0 75.0
1 75.0 73.0 100.0 98.0 NaN NaN
2 87.0 88.0 84.0 85.0 NaN NaN
3 NaN NaN 100.0 99.0 NaN NaN
4 NaN NaN 87.0 70.0 84.0 96.0
5 79.0 89.0 NaN NaN NaN NaNIn the above output, the Roll column has the same value in each row. Hence, this column is dropped from the output. To display all the columns in the resultant dataframe, you can assign the value True to the keep_shape parameter as follows.
import pandas as pd
myDicts1=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 82},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":75, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":87, "Physics":84, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 84},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":79, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df1=pd.DataFrame(myDicts1)
print("The first dataframe is:")
print(df1)
myDicts2=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":95, "Physics":92, "Chemistry": 75},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":73, "Physics":98, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":88, "Physics":85, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":99, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":70, "Chemistry": 96},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":89, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df2=pd.DataFrame(myDicts2)
print("The second dataframe is:")
print(df2)
output_df=df1.compare(df2,keep_shape=True)
print("The output dataframe is:")
print(output_df)Output:
The first dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 87 82
1 2 75 100 90
2 3 87 84 76
3 4 100 100 90
4 5 90 87 84
5 6 79 75 72
The second dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 95 92 75
1 2 73 98 90
2 3 88 85 76
3 4 100 99 90
4 5 90 70 96
5 6 89 75 72
The output dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
self other self other self other self other
0 NaN NaN 100.0 95.0 87.0 92.0 82.0 75.0
1 NaN NaN 75.0 73.0 100.0 98.0 NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN 87.0 88.0 84.0 85.0 NaN NaN
3 NaN NaN NaN NaN 100.0 99.0 NaN NaN
4 NaN NaN NaN NaN 87.0 70.0 84.0 96.0
5 NaN NaN 79.0 89.0 NaN NaN NaN NaNTo keep the original values for the columns that have equal values instead of NaN, you can assign the value True to the keep_equal parameter as shown below.
import pandas as pd
myDicts1=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 82},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":75, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":87, "Physics":84, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 84},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":79, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df1=pd.DataFrame(myDicts1)
print("The first dataframe is:")
print(df1)
myDicts2=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":95, "Physics":92, "Chemistry": 75},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":73, "Physics":98, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":88, "Physics":85, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":99, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":70, "Chemistry": 96},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":89, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df2=pd.DataFrame(myDicts2)
print("The second dataframe is:")
print(df2)
output_df=df1.compare(df2,keep_shape=True, keep_equal=True)
print("The output dataframe is:")
print(output_df)Output:
The first dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 87 82
1 2 75 100 90
2 3 87 84 76
3 4 100 100 90
4 5 90 87 84
5 6 79 75 72
The second dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 95 92 75
1 2 73 98 90
2 3 88 85 76
3 4 100 99 90
4 5 90 70 96
5 6 89 75 72
The output dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
self other self other self other self other
0 1 1 100 95 87 92 82 75
1 2 2 75 73 100 98 90 90
2 3 3 87 88 84 85 76 76
3 4 4 100 100 100 99 90 90
4 5 5 90 90 87 70 84 96
5 6 6 79 89 75 75 72 72You should remember that the dataframes can be compared only if their schema is the same. In other words, the dataframes that are being compared should have the same number of columns and the columns should be in the same order. Otherwise, the program will run into errors.
Similarly, if the dataframes have an equal number of columns, but they are not in the same order, the program will run into an exception.
Compare DataFrames Row-wise in Python
To show the output after comparing the dataframes row-wise, you can assign the value 1 to the align_axis parameter as shown below.
import pandas as pd
myDicts1=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":100, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 82},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":75, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":87, "Physics":84, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":100, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":87, "Chemistry": 84},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":79, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df1=pd.DataFrame(myDicts1)
print("The first dataframe is:")
print(df1)
myDicts2=[{"Roll":1,"Maths":95, "Physics":92, "Chemistry": 75},
{"Roll":2,"Maths":73, "Physics":98, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":3,"Maths":88, "Physics":85, "Chemistry": 76},
{"Roll":4,"Maths":100, "Physics":99, "Chemistry": 90},
{"Roll":5,"Maths":90, "Physics":70, "Chemistry": 96},
{"Roll":6,"Maths":89, "Physics":75, "Chemistry": 72}]
df2=pd.DataFrame(myDicts2)
print("The second dataframe is:")
print(df2)
output_df=df1.compare(df2,keep_shape=True, keep_equal=True, align_axis=0)
print("The output dataframe is:")
print(output_df)Output:
The first dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 100 87 82
1 2 75 100 90
2 3 87 84 76
3 4 100 100 90
4 5 90 87 84
5 6 79 75 72
The second dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 1 95 92 75
1 2 73 98 90
2 3 88 85 76
3 4 100 99 90
4 5 90 70 96
5 6 89 75 72
The output dataframe is:
Roll Maths Physics Chemistry
0 self 1 100 87 82
other 1 95 92 75
1 self 2 75 100 90
other 2 73 98 90
2 self 3 87 84 76
other 3 88 85 76
3 self 4 100 100 90
other 4 100 99 90
4 self 5 90 87 84
other 5 90 70 96
5 self 6 79 75 72
other 6 89 75 72
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to compare two dataframes in python. To learn more about python programming, you can read this article on dictionary comprehension in python. You might also like this article on list comprehension in python.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Stay tuned for more informative articles.
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

