JSON and XML files are used in software systems for data transmission, configuration management, and other tasks. This article discusses different ways to convert a JSON string or File to XML in Python.
What is JSON File Format?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data interchange format. It is a text format that is easy for humans to read and write, and easy for machines to parse and generate. JSON is commonly used for transmitting data between a server and a web application, or between different parts of a software system.
In a JSON file, data is represented as key-value pairs, where the key is a string and the value can be a string, number, boolean, array, or another JSON object. The values are separated by commas, and objects are enclosed in curly braces ({}) while arrays are enclosed in square brackets ([]).
Here is an example of a simple JSON object:
{
"employee": {
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 35,
"job": {
"title": "Software Engineer",
"department": "IT",
"years_of_experience": 10
},
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St.",
"city": "San Francisco",
"state": "CA",
"zip": 94102
}
}
}This JSON file contains details of an employee. You can observe that the data is stored as key-value pairs.
What is XML File Format?
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language that is used to store and transport data. Like JSON, it is a text-based format that is easy for humans to read and write, and can be parsed and generated by machines.
In an XML file, data is enclosed in tags, which describe the data and its structure. Each tag has an opening and a closing tag, and the data that is enclosed between the tags is called the element’s content. Attributes can be added to the opening tag to provide additional information about the element.
Here is an example of a simple XML document:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<employee>
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>35</age>
<job>
<title>Software Engineer</title>
<department>IT</department>
<years_of_experience>10</years_of_experience>
</job>
<address>
<street>123 Main St.</street>
<city>San Francisco</city>
<state>CA</state>
<zip>94102</zip>
</address>
</employee>In this XML, we have used the same data shown in the JSON file. You can observe that the elements in the XML files are stored using tags.
Convert JSON String to XML String in Python
To convert a JSON string to an XML string, we will first convert the json string to a python dictionary. For this, we will use the loads() method defined in the json module. The loads() module takes the json string as its input argument and returns the dictionary.
Next, we will convert the python dictionary to XML using the unparse() method defined in the xmltodict module. The unparse() method takes the python dictionary as its input argument and returns an XML string.
You can observe this in the following example.
import json
import xmltodict
json_string="""{"employee": {"name": "John Doe", "age": "35", "job": {"title": "Software Engineer", "department": "IT", "years_of_experience": "10"}, "address": {"street": "123 Main St.", "city": "San Francisco", "state": "CA", "zip": "94102"}}}
"""
print("The JSON string is:")
print(json_string)
python_dict=json.loads(json_string)
xml_string=xmltodict.unparse(python_dict)
print("The XML string is:")
print(xml_string)Output:
The JSON string is:
{"employee": {"name": "John Doe", "age": "35", "job": {"title": "Software Engineer", "department": "IT", "years_of_experience": "10"}, "address": {"street": "123 Main St.", "city": "San Francisco", "state": "CA", "zip": "94102"}}}
The XML string is:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<employee><name>John Doe</name><age>35</age><job><title>Software Engineer</title><department>IT</department><years_of_experience>10</years_of_experience></job><address><street>123 Main St.</street><city>San Francisco</city><state>CA</state><zip>94102</zip></address></employee>JSON String to XML File in Python
Instead of creating a string, we can also convert a JSON string to an XML file in python. For this, we will use the following steps.
- First, we will convert the JSON string to a python dictionary using the
loads()method defined in the json module. - Next, we will open an empty XML file using the
open()function. Theopen()function takes the file name as its first input argument and the literal“w”as its second input argument. After execution, it returns a file pointer. - Once we get the file pointer, we will save the python dictionary to an XML file using the
unparse()method defined in the xmltodict module. Theunparse()method takes the dictionary as its first argument and the file pointer as the argument to the output parameter. After execution, it writes the XML file to the storage. - Finally, we will close the XML file using the
close()method.
After executing the above steps, you can convert the JSON string to an XML file as shown below.
import json
import xmltodict
json_string="""{"employee": {"name": "John Doe", "age": "35", "job": {"title": "Software Engineer", "department": "IT", "years_of_experience": "10"}, "address": {"street": "123 Main St.", "city": "San Francisco", "state": "CA", "zip": "94102"}}}
"""
python_dict=json.loads(json_string)
file=open("person.xml","w")
xmltodict.unparse(python_dict,output=file)
file.close()The output file looks as follows.
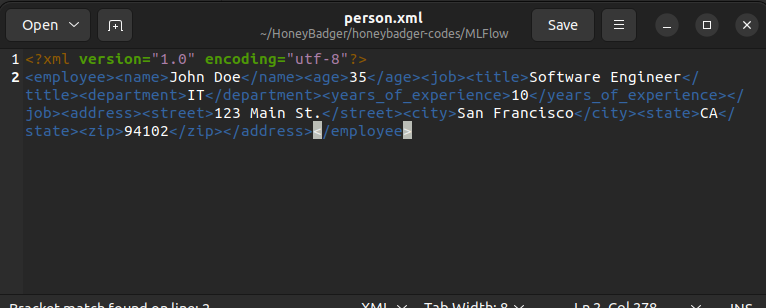
Convert JSON File to XML String in Python
To convert a JSON file to an XML string, we will first open the JSON file in read mode using the open() function.
The open() function takes the file name as its first input argument and the python literal “r” as its second input argument. After execution, the open() function returns a file pointer.
After this, we will load the json file into a python dictionary using the load() method defined in the json module. The load() method takes the file pointer to the JSON file as its input argument and returns a python dictionary.
Once we get the python dictionary, we will convert it to an XML string using the unparse() method from the xmltodict module.
We will convert the following JSON file to XML.
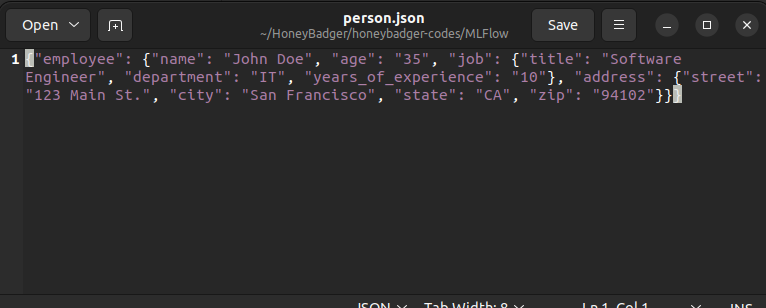
All the steps discussed above have been implemented in the following example.
import json
import xmltodict
file=open("person.json","r")
python_dict=json.load(file)
xml_string=xmltodict.unparse(python_dict)
print("The XML string is:")
print(xml_string)Output:
The XML string is:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<employee><name>John Doe</name><age>35</age><job><title>Software Engineer</title><department>IT</department><years_of_experience>10</years_of_experience></job><address><street>123 Main St.</street><city>San Francisco</city><state>CA</state><zip>94102</zip></address></employee>JSON File to XML File in Python
To convert a JSON file to an XML file, we will use the following steps.
- First, we will open the JSON file in read mode using the
open()function. For this, we will pass the filename as the first input argument and the literal “r” as the second input argument to theopen()function. Theopen()function returns a file pointer. - Next, we will load the json file into a python dictionary using the
load()method defined in the json module. Theload()method takes the file pointer as its input argument and returns a python dictionary. - Now, we will open an XML file using the
open()function. Then, we will save the python dictionary to the XML file using theunparse()method defined in the xmltodict module. - Finally, we will close the XML file using the
close()method.
After executing the above steps, we can convert the JSON file to an XML file in Python. You can observe this in the following example.
import json
import xmltodict
file=open("person.json","r")
python_dict=json.load(file)
xml_file=open("person.xml","w")
xmltodict.unparse(python_dict,output=xml_file)
xml_file.close()After executing the above code, the content of the JSON file "person.json" will be saved as XML in the "person.xml" file.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed different ways to convert a JSON string or File to XML in Python. To learn more about file conversions, you can read this article on how to convert YAML to JSON in Python. You might also like this article on how to convert JSON into a python dictionary.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Stay tuned for more informative articles.
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

