YAML is a data serialization format used to store and transmit data in a human-readable and easy-to-write format. We can store and transmit python objects using YAML format. In this article, we will discuss how to convert a python dictionary to YAML format.
What is the YAML Format?
YAML is a data format commonly used for configuration files, data exchange between systems, and in modern application development as an alternative to JSON and XML.
YAML’s syntax is simple, clean, and readable. It uses indentation to define the structure of the data, making it easy to see the relationships between different elements. The syntax is also very flexible, allowing for the representation of simple scalar values (such as strings, numbers, and booleans) as well as complex data structures, such as lists and dictionaries.
Following is an example of a YAML file.
employee:
name: John Doe
age: 35
job:
title: Software Engineer
department: IT
years_of_experience: 10
address:
street: 123 Main St.
city: San Francisco
state: CA
zip: 94102
The above YAML file describes information about an employee.
- The top-level key
employeemaps to an object that contains information about the employee, including their name, age, job, and address. - The
namekey maps to the string value John Doe, which is the employee’s name. Theagekey maps to the integer value 35, which is the employee’s age. - The
jobkey maps to an object that contains information about the employee’s job. This object includes the employee’s job title, department, and years of experience. - The
addresskey maps to an object that contains information about the employee’s address. This object includes the employee’s street, city, state, and zip code.
The corresponding python dictionary for the above YAML file looks as follows.
employee_dict={'employee': {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 35,
'job': {'title': 'Software Engineer','department': 'IT','years_of_experience': 10},
'address': {'street': '123 Main St.', 'city': 'San Francisco','state': 'CA', 'zip': 94102}}}
Let us now discuss how to convert a dictionary to a YAML string or file.
Python Dictionary to a YAML String
To convert a python dictionary into a YAML string, we can use the dump() method defined in the yaml module. The dump() method takes the dictionary as its input argument and returns the YAML string after execution. You can observe this in the following example.
import yaml
employee_dict={'employee': {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 35,
'job': {'title': 'Software Engineer','department': 'IT','years_of_experience': 10},
'address': {'street': '123 Main St.', 'city': 'San Francisco','state': 'CA', 'zip': 94102}}}
print("The python dictionary is:")
print(employee_dict)
yaml_string=yaml.dump(employee_dict)
print("The YAML string is:")
print(yaml_string)Output:
The python dictionary is:
{'employee': {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 35, 'job': {'title': 'Software Engineer', 'department': 'IT', 'years_of_experience': 10}, 'address': {'street': '123 Main St.', 'city': 'San Francisco', 'state': 'CA', 'zip': 94102}}}
The YAML string is:
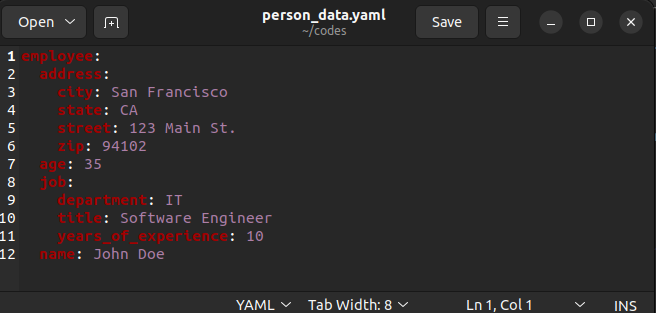
employee:
address:
city: San Francisco
state: CA
street: 123 Main St.
zip: 94102
age: 35
job:
department: IT
title: Software Engineer
years_of_experience: 10
name: John DoeConvert Dictionary to YAML File in Python
We can also use the dump() method to convert a python dictionary to a YAML file. For this, we will use the following steps.
- First, we will open a YAML file in write mode using the
open()function. Theopen()function takes the file name as its first input argument and the python literal “w” as its second input argument. After execution, it returns a file pointer. - Once we get the file pointer, we will pass it to the
dump()method as the second input argument and the dictionary will be the first input argument. After execution, thedump()method will save the contents of the dictionary in YAML format. - Finally, we will close the file using the
close()method.
You can observe the entire process in the following example.
import yaml
employee_dict={'employee': {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 35,
'job': {'title': 'Software Engineer','department': 'IT','years_of_experience': 10},
'address': {'street': '123 Main St.', 'city': 'San Francisco','state': 'CA', 'zip': 94102}}}
print("The python dictionary is:")
print(employee_dict)
file=open("person_data.yaml","w")
yaml.dump(employee_dict,file)
file.close()
print("YAML file saved.")Output:
The python dictionary is:
{'employee': {'name': 'John Doe', 'age': 35, 'job': {'title': 'Software Engineer', 'department': 'IT', 'years_of_experience': 10}, 'address': {'street': '123 Main St.', 'city': 'San Francisco', 'state': 'CA', 'zip': 94102}}}
YAML file saved.The output YAML file looks as follows.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to convert a python dictionary to a YAML string or file.
To learn more about python programming, you can read this article on how to convert JSON to YAML in Python. You might also like this article on custom json encoders in python.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Stay tuned for more informative articles.
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

