Python is a very rich language in terms of features and data structures. It has a lot of inbuilt data structures like Python dictionary, list, tuple, set, frozenset, etc. Apart from that, we can also create our own custom data structures using Classes. In this article, we will learn about Binary tree data structure in Python and will try to implement it using an example.
What is a Tree Data Structure?
A Python tree is a data structure in which data items are connected using references in a hierarchical manner in the form of edges and nodes. Each tree consists of a root node from which we can access the elements of the tree. Starting from the root node, each node contains zero or more nodes connected to it as children.
A simple binary tree can be depicted as seen in the following figure.
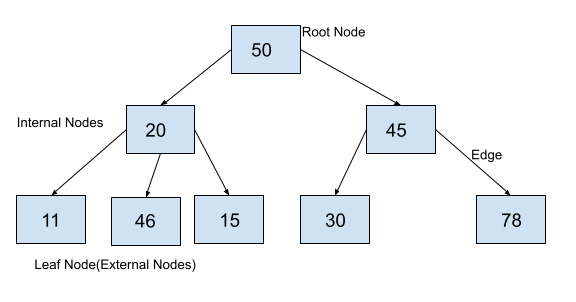
Parts of a Tree Data structure
A tree consists of a root node, leaf nodes, and internal nodes. Each node is connected to its child via a reference, which is called an edge.
Root Node: The root node is the topmost node of a tree. It is always the first node created while creating the tree and we can access each element of the tree starting from the root node. In the above example, the node containing element 50 is the root node.
Parent Node: The parent of any node is the node that references the current node. In the above example, 50 is the parent of 20 and 45, and 20 is the parent of 11, 46, and 15. Similarly, 45 is the parent of 30 and 78.
Child Node: Child nodes of a parent node are the nodes at which the parent node is pointing using the references. In the example above, 20 and 45 are children of 50. The nodes 11, 46, and 15 are children of 20 and 30 and 78 are children of 45.
Edge: The reference through which a parent node is connected to a child node is called an edge. In the above example, each arrow that connects any two nodes is an edge.
Leaf Node: These are those nodes in the tree that have no children. In the above example, 11, 46, 15, 30, and 78 are leaf nodes.
Internal Nodes: Internal Nodes are the nodes that have at least one child. In the above example, 50, 20, and 45 are internal nodes.
What is a Binary Tree in Python?
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node can have a maximum of 2 children. It means that each node in a binary tree can have either one, or two or no children. Each node in a binary tree contains data and references to its children. Both the children are named as the left child and the right child according to their position.
The structure of a node in a binary tree is shown in the following figure.
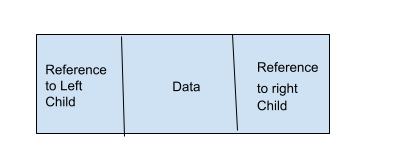
We can define a Tree node of the structure shown above in Python using classes as follows.
class BinaryTreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild=NoneHere, the constructor of the Tree node takes the data value as input, creates an object of BinaryTreeNode type and initializes the data field equal to the given input, and initializes the references to the children to None. The children can be assigned to the nodes later.
An example of a binary tree is shown in the figure below.
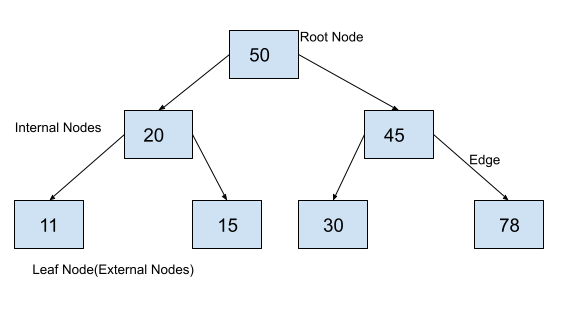
We can implement the above binary tree in Python as follows.
class BinaryTreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
node1 = BinaryTreeNode(50)
node2 = BinaryTreeNode(20)
node3 = BinaryTreeNode(45)
node4 = BinaryTreeNode(11)
node5 = BinaryTreeNode(15)
node6 = BinaryTreeNode(30)
node7 = BinaryTreeNode(78)
node1.leftChild = node2
node1.rightChild = node3
node2.leftChild = node4
node2.rightChild = node5
node3.leftChild = node6
node3.rightChild = node7
print("Root Node is:")
print(node1.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node1.leftChild.data)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node1.rightChild.data)
print("Node is:")
print(node2.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node2.leftChild.data)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node2.rightChild.data)
print("Node is:")
print(node3.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node3.leftChild.data)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node3.rightChild.data)
print("Node is:")
print(node4.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node4.leftChild)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node4.rightChild)
print("Node is:")
print(node5.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node5.leftChild)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node5.rightChild)
print("Node is:")
print(node6.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node6.leftChild)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node6.rightChild)
print("Node is:")
print(node7.data)
print("left child of the node is:")
print(node7.leftChild)
print("right child of the node is:")
print(node7.rightChild)
Output:
Root Node is:
50
left child of the node is:
20
right child of the node is:
45
Node is:
20
left child of the node is:
11
right child of the node is:
15
Node is:
45
left child of the node is:
30
right child of the node is:
78
Node is:
11
left child of the node is:
None
right child of the node is:
None
Node is:
15
left child of the node is:
None
right child of the node is:
None
Node is:
30
left child of the node is:
None
right child of the node is:
None
Node is:
78
left child of the node is:
None
right child of the node is:
NoneHow to Traverse a Binary Tree in Python?
We use different tree traversal algorithms to traverse a binary tree in Python. To understand the traversal algorithms, you need to understand the concept of recursion in Python.
You can read the implementation of all these tree traversal algorithms in Python using the following links.
- Pre-Order Tree Traversal in Python
- Post Order Tree Traversal in Python
- Level Order Tree Traversal in Python
- In Order Tree Traversal in Python
Different Operations on A Binary Tree in Python
Binary trees are a complex data structure and operations on binary trees can also be complex. Hence, we use a special type of binary tree called a binary search tree to implement a binary tree in Python. We can add elements to a binary search tree, search for an element, update an element, and delete an element from a binary tree. You can learn how to add an element and search for an element in a binary search tree in this article on binary search trees in Python.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed tree data structure and binary tree data structure in Python. To learn more about data structures in Python, you can read this article on linked list in Python. You might also like this article on Python continue vs break statements.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. Stay tuned for more informative articles.
Happy Learning!
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

