In Python, you can access a file by using the open() method. However, using the open() method requires you to use the close() method to close the file explicitly. Instead, you can create a context using the with Open statement in Python. In this article, we will discuss how we can automatically open, read, and close a file using the with statement and the open() function in Python.
The With Statement in Python
We use the with statement in Python to create a context. Whatever statements we execute inside the context created using the with statement does not affect the outer environment. The with statement simplifies exception handling by encapsulating common preparation and cleanup tasks. Hence, you can get better syntax and exception handling by using the “With” statement in Python.
The open() Function in Python
We use the open() function to open a file in Python. It takes the filename as its first input argument and the python literals “r”, “w”, “r+”, etc as its second input argument to specify the mode in which the file is opened. After execution, it returns a file pointer.
We can use the file pointer to read from the file or write data to the file. For example, consider that we have the following text file.
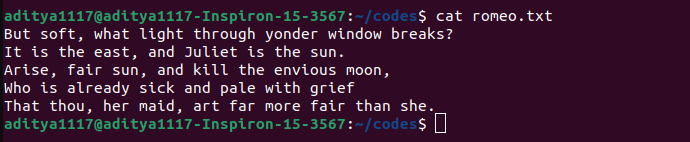
In the above file, we have five lines of text, let us open the file using the open() function and read the file contents. For this, we will write the following code in open_example.py file and execute it.
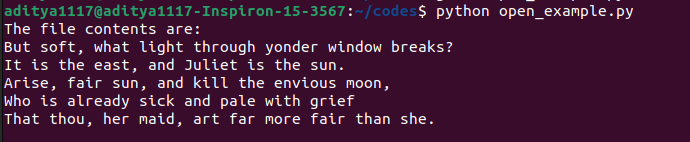
file = open("romeo.txt","r")
data = file.read()
print("The file contents are:")
print (data)
file.close() # It's important to close the file when you're done with itOnce we execute the above code, it prints the output of the romeo.txt file as shown below.
When we use the open() statement, we also need to close the file using the close() method. Otherwise, the file may get corrupted. Also, if we write any data to the file and don’t close it, the contents written to the file will not be saved. Hence, it is really important to close the file.
However, we might forget to use the close() statement to close the file. In such a case, we can lose data or even corrupt the file. To avoid this, we can create a context using the with statement and open a file inside it using the open() function. Let us discuss how to use the with statement and the open() function together in Python.
With Statement Usage with Open() Function in Python
As discussed earlier, whatever we do inside the context created using the with statement stays inside the context. Hence, we can also use the with statement with the open() function in Python to open a file, perform operations on it, and close it. The syntax for using the with statement is as follows.
with open(filename, mode) as myFile:
//read from the file
// write to the file.In the above syntax, the file is opened, and the file pointer is assigned to the myFile variable. Then, we can perform read and write operations on the file using the myFile object. When all the statements inside the with block are executed, the file is automatically closed.
For example, we can rewrite the code used in the previous example using the with statement and the open() function as shown below.
with open("romeo.txt","r") as file:
data=file.read()
print("The file contents are:")
print(data)
The above code works in the same manner as the previous code without the need to use the close() method. Hence, combining the with statement and the open() function in Python helps us read and write to the file without being worried about closing it.
In the above code, you can observe that we have opened the romeo.txt file using the with open statement. The statement returns a file pointer that is assigned to the variable “file”. Now, we can perform any operation on the file object inside the context of the with statement. Once all the statements are executed and the execution reaches the end of the with context block, the file is automatically closed by the Python interpreter.
Also, if the program runs into any exception inside the with block, the with open context in Python closes the file before terminating the program. In this way, the data inside the file remains safe even if the program is terminated abruptly. Notice, that we didn’t have to write “file.close()”. That will automatically be called.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how you can use the with open statement instead of the open()
method to open a file in Python. To learn more about Python programming, you can read this article on string manipulation in Python. You might also like this article on Python if else shorthand.
Recommended Python Training
Course: Python 3 For Beginners
Over 15 hours of video content with guided instruction for beginners. Learn how to create real world applications and master the basics.

